Use the golden ratio
Very precise speaker placement can open up a whole new dimension in listening, so I will outline the system that is becoming the standard of the industry. This standardized listening room is a Golden Cuboid and is the model of math used in the system. This method will work with any panel or box speaker, in any reasonably sized rectangular room. You may find that you have already positioned your speakers this way by ear.
Active nodes are the main concern when placing speakers in a rectangular room. A node, or the frequency where speakers and parallel walls interact, is proportional to the speaker to the wall distance.

The three most importance nodes, in order of importance, are proportional to the distance between the speaker and:
- The side wall nearest the speaker
- The rear wall
- The side wall across from the speaker
A secondary factor is the speaker-to-speaker time constant.
When you use this method to set your room up, the speakers are placed so the three nodes progress or differ from one another in Golden Ratio. This eliminates any unison or near unison resonance in the nodes.
Speaker placement, simply stated.
- The distance from the center of the woofer face to the side walls is:
- Room Width (RW) x .276
- The distance from the center of the woofer face to the wall behind the speaker is:
- Room Width (RW) x .447
This is all you need to know to place speakers in a symmetrical, rectangular room. Don’t look at diagrams B, C, D, and E until you have your speakers in position, because it will make your head explode!
For those who must know more…
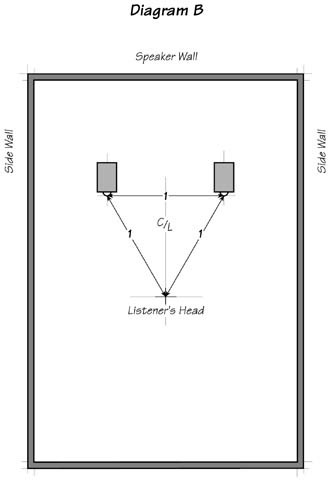
Placing speakers in this manner will set all the nodes in Golden progression. Final focusing can be done from the near field position (Diagram B)
In the near field position the speakers and the listener’s head are the points of an equilateral triangle. Near field listening gives the perfect stereo field. It is frequently used in the recording studio to position the microphones and the voice in the mix. The near field listening position is determined by the “center to center” distance of the speakers and the distance to the listener’s head. It does not refer to the room in any way.
The importance of symmetrical speaker placement in a small room cannot be over emphasized. Once the speakers are set as close to perfect as possible, you must angle them slightly toward the listening position. This can be done by ear and usually a 1/4 to 1/2 inch tweak will do. Box speakers generally require a bit more toe-in than planear speakers. You will be able to hear a center focused voice clarify when the sweet spot is hit.
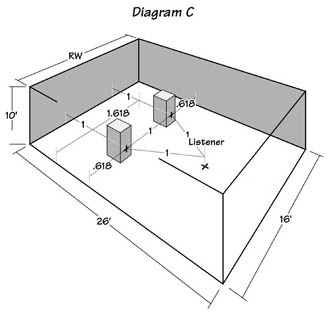
10.000 (H) x 16.18033989 (W) x 26.18033989 (L)
Golden Cuboid Listening Room
The Golden Cuboid listening room (Diagram C) is: 10′ x 16′ x 26′ or precisely as 10.000 (H) x 16.18033989 (W) x 26.18033989 (L).
Its dimensions differ in a Golden Ratio or Fibonacci sequence (5-8-13-21-34…). The three major room nodes progress or differ in Golden Ratio and thus null rather than add or beat.
The math used to create the dimensions of the Golden Cuboid listening room can also be applied to speaker placement, speaker box size, or for that matter, the conductors in your audio cable. Doing so will make the node progression an irrational or Golden progression.
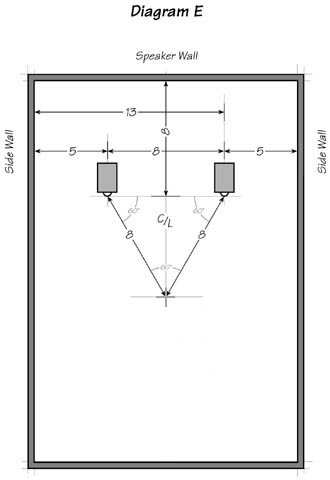
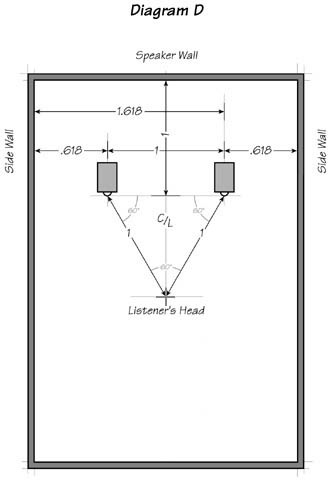
In the case of our listening room, the relationship of potential nodes or energy storage units can be expressed as a ratio (Diagram D), or a Fibonacci progression (Diagram E)
Golden Ratio can be derived from an exponential progression known as the Fibonacci sequence or summation numbers: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89… etc. The farther you go, the closer the distance between the numbers approaches the ratio that can never be reached: 1.618033988… to infinity, to 1. The Golden listening room is 10′ x 16′ x 26′. This can be reduced to 5 x 8 x 13.
Distance x Ratio = Numerical (Percentage)
Speaker to side wall:
RW x .618 = 5 (.276)
Speaker to rear wall:
RW x 1 = 8 (.447)
Speaker to opposite wall:
RW x 1.618 = 13 (.724)
Speaker to speaker:
RW x 1 = 8 (.447)
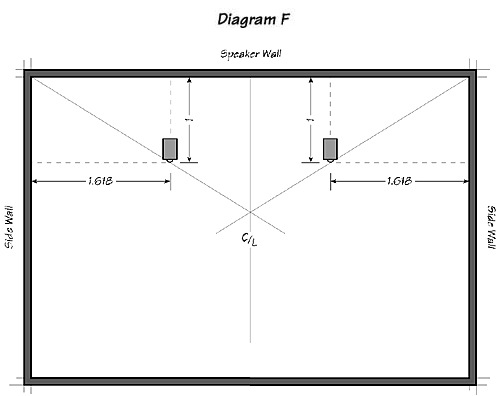
If you are forced to place your speakers on the long side of a symmetrical, rectangular room, create a Golden rectangle in each rear corner. Your speakers can then be placed anywhere along a line extending from the outside rear corner through the inside front corner (Diagram F).
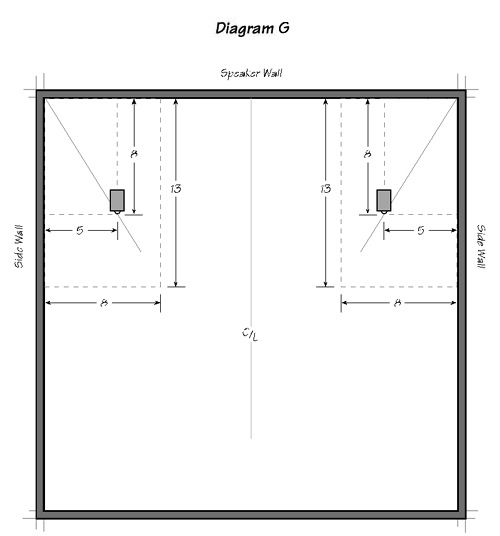
If you have the misfortune to have a square listening room, as above, create Golden Rectangles in the rear corners of the room. Your speakers can then be placed along lines extending from the outside rear corners through the inside front corners (Diagram G).
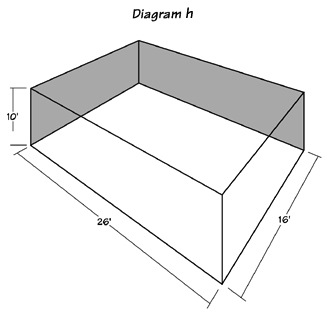
The Golden Cuboid (Diagram H) is the best “rectangular” shape for a listening room. If, however, you have full architectural freedom, a Golden Trapagon (Diagram I) is by far the favored shape. A Golden Trapagon has a Golden rectangle for the front wall behind the speakers, and the room progresses to a larger (by Golden Ratio in area) Golden rectangle back wall behind the listener.
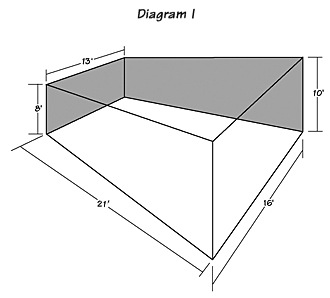
For example, if the wall behind the speakers is 10 feet x 16 feet, the room would then be 26 feet long and the wall behind the listener would be 13 feet x 21 feet. Ideally, the rear portion of this room would vent into an attic space filled with fiberglass insulation.
The trick to a Golden Trapagon shaped room is it eliminates the problem of parallel walls and the slap and sharp nodes associated with them. The “sound” of this room is a decaying hologram of the original, not a slap. This decay is exponential, or higher, at all frequencies. The relationship between the height and the width of the room, at any point, is Golden Ratio. The cross-section area at the rear of the room is 1.618 times the cross-section of the front. In the example above, the ceiling height would be 12.72 feet.
The ratio of front height or width, to rear height or width, is 1.272 to 1. 1.272 is the square root of 1.618 or Golden Ratio. The progression of size at the ends of the room is a area relationship. The sound confronts the entire surface of the end walls at the same time, rather than progressively as with height and width. It is like tuning a guitar to a major chord, the side walls become the strings and the end walls are the bridge and tailpiece.
by George Cardas, Owner of Cardas Audio





































shadowfox64
March 20, 2013 at 12:22 am
Not many people maybe realize this, but this is a “golden story” for any audiophile!
If you follow these tips you will get for sure into the ballpark.
Thanks George and happy listening, a world that few enjoy!
Chuck
October 27, 2022 at 6:46 pm
I would like to see the “real” numbers for a real golden cube. Axial, tangential and oblique nodes. Frequencies?